

Human talent management model based on intrinsic motivation for the professional performance of teachers.
Sinergias educativas, vol.. 6, no. 2, 2021
Universidad de Oriente


Received: 03 May 2020
Accepted: 24 November 2020

Abstract: Today educational institutions must face a series of challenges and difficulties, as a result of the changing environment, globalization and their ideal of effective positioning within the knowledge society. To face the new context, pedagogical leaders must develop motivational competencies that lead to develop in their teachers better performances driven by intrinsic motivation. The objective of this study is to propose a Human Talent Management Model by Intrinsic Motivation for Professional Teacher Performance that promotes the development of motivational competence and competitiveness of the educational institution. The study is of descriptive design, of a propositional type, the study sample is made up of 19 people among teachers and directors of the Primary and Secondary Educational Institution "Pedro Ruiz Gallo" of Muy Finca-Mochumì. The results of the research have made it possible to analyze relevant aspects of the reality of human talent management, intrinsic motivation and teaching performance at the global, Latin American, national and local levels in order to prepare the proposal in which the management characteristics of the human talent by intrinsic motivation based on new dimensions resulting from the relationship between them.ç
Keywords: Management model, human talent, intrinsic motivation, professional performance, teachers.
Resumen: Hoy las instituciones educativas deben enfrentar una serie de desafíos y dificultades, como producto del entorno cambiante, la globalización y su ideal de posicionamiento efectivo dentro de la sociedad del conocimiento. Para enfrentar el nuevo contexto los líderes pedagógicos deben desarrollar competencias motivacionales que conlleven a desarrollar en sus docentes mejores desempeños impulsados por la motivación intrínseca. El objetivo del presente estudio es proponer un modelo de gestión del talento humano por motivación intrínseca para el desempeño profesional docente que promueva el desarrollo de la competencia motivacional y la competitividad de la institución educativa. El estudio es de diseño descriptivo, de tipo propositiva, la muestra de estudio lo conforma 19 personas entre docentes y directivos de la institución educativa primaria y secundaria “Pedro Ruiz Gallo” de Muy Finca- Mochumí. Los resultados de la investigación, han permitido analizar aspectos relevantes de la realidad de la gestión de talento humano, la motivación intrínseca y desempeño docente a nivel mundial, latinoamericano, nacional, local con la finalidad de elaborar la propuesta en la destaca características de gestión del talento humano por motivación intrínseca basado en nuevas dimensiones resultado de la relación entre ellas.
Palabras clave: Modelo de gestión, talento humano, motivación intrínseca, desempeño profesional, docentes.
Introduction
Economic and social changes are transforming the management of educational institutions in the management of human talent to achieve better performance and meet the new challenges of the context, which require greater creativity and initiative, and commitment of teachers. Currently, the professional requirements assigned by the control bodies of higher education, generate concern and increase the level of anxiety in university teachers, because they must play various roles, which represent greater cooperation in management procedures and decision making corresponding to the teaching - learning process. (Molina and García, 2018). In addition, there is a concern in educational environments to better respond to the demands of the productive sector and the requirements of employers, rethinking traditional curricular designs. (López and Narváez, 2019). In the educational field there are many proposals, however they do not represent profitable results in our society, success has not been achieved. (Alvarez, Gudiño, Macías and Izquierdo, 2020).
Therefore, Marcelo & Vaillant (2009) state that social transformations require an in-depth review of human talent management with respect to teaching performance and working conditions, teaching performance and motivations to reach the highest levels of productivity. One of the factors that influence the professional performance of teachers is motivation, since it is necessary to recover the passion of teachers for their work, an aspect that has not been achieved only with extrinsic motivation and that requires, according to the latest research, the awakening of intrinsic motivation in schools, since economic incentives are not giving the expected results in the performance of teachers.
The topicality of the problem lies in the need for educational institutions to awaken motivation, create a culture of motivation and establish exercises to stay motivated in front of the task or activities as an important dimension of the professional performance of teachers in service of the institutions.
Educational organizations continue to manage human talent as an organizational resource without taking into account that we are human beings with inherent faculties such as intelligence, knowledge, skills, personality, aspirations, abilities, feelings, aspirations, emotions and self-perceptions. Likewise, there are variables that have a decisive influence on job performance. In our case, they have an influence on teachers' work deployment, such as motivation, which is an aspect neglected by many pedagogical leaders and which today is of great importance to achieve excellent performance.
Currently, extrinsic motivational practices based on rewarding the worker through compensation and economic incentives such as prizes, commissions or bonuses for good performance and punishment in case of failure, is what has traditionally been applied. This way of managing talent responded efficiently to the industrial historical moment in front of the routine and recurrent mechanical activity; that is, those that we execute with the (left) hemisphere of our brain center.
Latin American education has been affected by reform processes that have generated uncertainty, setbacks and wear and tear in the teaching profession. "Many teachers in Latin America have had to adapt to the reforms without the necessary preparation and as a result have had great difficulties that have affected them personally and professionally, producing a high level of job demotivation" (Gomez, 2008, p.88).
Today, teachers are under pressure to use new technologies and methodologies, to work collegially, to give more of their time to planning and extracurricular activities, to research work, and to the disciplinary control (behavior) of students and the lack of parental support. This has generated frustration, demotivation and dissatisfaction among teachers who feel limited in their capacity to respond to the new context that is affecting their performance, as they show little commitment to their work, weak leadership and initiative, lack of interest in teamwork, self-preparation, research and innovation, probably due to an inefficient practice of human talent management to face the new educational challenges. One of the aspects that are influencing this reality are the scarce motivational practices within the educational institution and the economic incentives that are only for a few and generate dissatisfaction among teachers who do not receive them when comparing that they do the same work but with different salaries. In addition, some teachers who receive greater economic benefits and are on a higher teaching scale do not necessarily demonstrate better performance; on the contrary, there is no greater effort, but rather the effort ended when they received the economic incentive. Internally, the educational institution has incentives and sanctions established in the internal regulations in force that correspond to the delivery of medals, congratulatory letters, diplomas, resolutions, and application of legal provisions for sanctions. These scarce recognitions are not granted regularly and when they are granted it is not on the basis of performance but for having fulfilled a work commission and in a general way. This leads to inequity and dissatisfaction, division and a negative attitude towards anything that means more effort and time outside the workload. It seems that teaching functions are only fulfilled because of the salary received at the end of each month.
The work plan also lacks objectives and activities related to training, updating, specialization, training and development of human talent on the part of the educational institution, since it does not have the financial resources. These actions have always been organized by the local Management Unit.
In conclusion, the educational institution has an inefficient and informal human talent management with extrinsic motivational practice based only on formally regulated rewards and incentives that do not have a positive influence on the performance of teachers, there is no motivational competence in teachers and the organization does not show competitiveness in its environment.
The problem of this research is how should be a model of human talent management by intrinsic motivation to improve the professional performance of teachers of the Educational Institution Pedro Ruiz Gallo de Mochumí - 2017?
Berrú, Campos and Seminario (2013) focus their study on the relationship between intrinsic motivation and job satisfaction of teachers at the educational institution Albert Einstein College, José Leonardo Ortiz. The research corresponds to the quantitative nature using a descriptive correlational design. A sample of 18 teachers was selected and the Steers R. and Braunstein D. Motivation Scale and the Job Satisfaction Scale (SL-SPC) were used as data collection instruments, concluding that female teachers between 26 and 30 years of age are factors that can exert a certain influence on the levels of intrinsic motivation and job satisfaction. The levels of job motivation in teachers fluctuate between medium values 44.4% and low 44.4%. The levels of job dissatisfaction are very high for the task significance factor with 61.1%, indicating that these teachers do not have expectations in their job performance. After the application of Pearson's tests, a result of 0.812 was obtained, which is a high correlation indicator, so there is a significant and positive relationship between intrinsic motivation and job satisfaction of teachers.
Herrera (2011) also presents his research: Motivation, satisfaction and work environment at the IE Karl Weiss - Chiclayo, conducted in a population of 65 teachers, the technique used was the interview. The research concluded that 48% of the teachers of the educational institution have a medium level of motivation, with the dimensions of identity and autonomy being the most significant, while the dimensions of feedback, importance and variety of the task characterize the low level of motivation. The dimensions that generate medium motivation in teachers are characterized by identity, which is related to the importance of the results they achieve with their work and the opportunities it offers them for their personal fulfillment; and autonomy, a dimension under which they consider that the responsibility with which they assume their work enables them to make decisions with the degree of freedom generated by their competencies. It is determined in the research that the appointed teacher shows less interest than the hired teacher because he/she feels secure in his/her job. In addition, the main reason why workers provide services to their educational institution is because of their need for a secure salary from the State; they point out that they make an effort to ensure that things go well but feel that they are not recognized. They recommend implementing better talent management processes that consider processes and activities aimed at improving the categories that were found at the medium level in relation to motivation. Especially those related to intrinsic motivation, which influences the employee's job satisfaction in the company.
Currently, the paradigm is based on the reason that organizations have competence through people. From here it is highlighted that the success of an organization depends on the capacity it has to manage the human capital or talent. It is important to point out that the potential of people is the core factor in the organization and development of the company's management, taking into account that business entities compete and develop in competitive environments. The management of human talent has progressed emerging new techniques such as Management by Labor Competencies, which provides solutions to organizations, is involved in the progress of employees and helps to increase the potential, for the achievement of personal goals and therefore of the organization. (López, 2018).
There are three approaches that guide the management theory used in the performance of people in the organization. According to Lewis and Heckman (2006) they are: Talent management vs. human resources practice, talent preservation vs. career plans and Talent linked to performance: 1) The first approach: considers talent management a way of managing human resources whose processes are: recruitment, selection, development and management of development and succession plans. 2) Second approach: preserving talent. It has at its core the idea of retaining talent in an organization as a core practice for the company to be successful. 3) Regarding the third approach, along the lines, "The need to improve the internal market in the organization based on the satisfaction of the needs of human talent, in an organizational climate conducive to the achievement of organizational objectives".
the human resource is a competent capacity to be transformed into a business advantage for competitiveness and productivity; therein lies the importance therefore if the human resource is willing to provide its effort, the organization will advance. (Solis, 2019). A management model integrated by people and based on competencies, considers that the objectives and planning of human resources must be built from the framework of the strategic objectives and plans of the company. An efficient talent management of human resources in higher education constitutes a primary objective, because it integrates the creation, dissemination and learning of new knowledge, and favors local, national and universal development, responding to the changes that originate at the global level. (Moreno and Sanchez, 2019). Therefore, the human resources management function must be aligned with the rest of the company's functions, being people and their knowledge a preponderant factor of productivity and a determining factor when establishing competitive advantages".
There are many theories of motivation and each of them differs in terms of the factor they consider most important in achieving motivation. A review of the different schools shows that some have focused on the motivational factors and others on the process; in any case, motivational models are moving towards giving great importance to the cognitive dimension. The best known theories are: the "X" "Y" Theory of Douglas Mc Gregor, which focuses its vision on two opposing positions underlying the life of human beings: positive position (X) and negative position (Y); the Hierarchy Model (Maslow, 1943) who conceives the individual as an integrated whole, which has a series of stable motives that guide him towards the future, prevailing as a motive of his activity, autonomy (possibility of fully using the skills, abilities and creativity). The criterion of self-realization is the supreme motive in his hierarchy of needs, he considers it the ultimate goal of learning to fully developed personality that is associated with an essence of intrinsic nature. (p.48); McClelland's (1961) theory of learned needs, which considers that "motivational drives are related to needs for Achievement, Affiliation and Power. The defining characteristics of the achievement-oriented are the pursuit of personal responsibility and the overcoming of challenges in order to reach attainable goals" (p.44); Herzberg's (1959) theory of motivation-hygiene focuses its theoretical construct on the work of the individual and the surrounding environment (externally oriented approach). From this research it was concluded that favorable situations were directly related to motivational variables (at work). For example, level of responsibility, progress, recognition, etc. On the other hand, unfavorable situations were related to hygiene variables (work context). Verbigracia, working condition, monitoring received, payment or salary, etc.
There are many challenges that teachers face when working with diverse groups in terms of origin, social status, religion and experiences; these determine motivations such as focusing on grades or pleasing parents; ideally, motivation should be intrinsic, characterized by autonomy. Motivational factors for education are the educational and family environment, in addition to personal components and different mechanisms of the context that influence and accompany the process. (Rojas and Hernández, 2020). Robbins (2005) states that "motivation is constituted by the processes responsible for an individual's desire to make a great effort to achieve organizational goals, conditioned by the capacity of the effort to satisfy some individual need" (p.292).
This means that there are variables or factors involved in motivation such as the needs of the individual must be compatible with the objectives of the organization, it depends on this to originate, guide and maintain motivation over time, if this does not happen, no matter how much effort is made, the results may be unfavorable or contrary to the interests of the same. Some work to satisfy their basic needs for survival, while others seek security; still others work to satisfy their own ego or something even deeper. The factors that move an individual to work cannot be reduced to a purely economic motivation. Gamboa Romero, M. A., Barros Morales, R. L., & Barros Bastidas, C. (2016). (Deci and Ryan, 1985, p.10).
It has a theoretical value because it contributes with a proposal for a human talent management model based on intrinsic motivation to contribute to the strengthening of the professional performance of in-service teachers, thus seeking their personal and professional satisfaction with their educational work. This model is based on scientific research at the level of organizational psychology and educational administration centered on truth criteria proposed by various authors who develop the subject in depth. It is assumed here that meaningful learning and efficient performance in human talent management are achieved not only with extrinsic incentives, since intrinsic interest in the task or activity is lost. Without internal motivation, no incentive will generate greater motivation. Intrinsic motivation is more concerned with internal satisfaction and less with external rewards. Daniel Pink highlights three important elements: autonomy, mastery and goals for the development of intrinsic motivation, in addition to the fundamental element of affectivity, which are present in the research.
From a practical point of view, this study justifies the research because it helps to solve an educational social problem linked to poor teaching performance. Importance should be given to the teaching performance since it represents a factor for the development of the student and his professional future, mentions that education has problems among them school failure, where students have problems to adapt to the requested conditions and to achieve the required results, becoming victims of exclusion. (Bedor, 2018). Professional performance is all work executed by an individual to respond to the tasks assigned as a commitment and that will be evaluated according to the result, the professional teaching performance is the action of the teacher according to his pedagogical capabilities to guide, guide, and evaluate the course of instruction of the student, he must know the specific functions for the teaching work. (Martínez and Guevara, 2015). The teacher's evaluation of the pedagogical practice will show the particular knowledge and the way he/she deliberates on his/her contexts and reformulates this particular knowledge. (Dimaté, Tapiero, González, Rodriguez & Arcila, 2017) The teacher needs a foundation of his professional identity, which is constituted by personal experiences, initial training and practice, it is essential to recognize his practice to reconstruct and model his identity, associate his particularity and how he expresses himself before the collective to which he belongs. (Marroquín, 2019)
The establishment of a Human Talent Management model based on Intrinsic Motivation directly results in the strengthening of self-esteem, in the social demand to generate commitments, in the creative capacity, in the satisfaction and competence of teachers. It will contribute to face the new challenges of the educational reforms that are being implemented by the Ministry of Education, resulting in the strengthening of student learning. For pedagogical leaders, it will be a strategic tool to generate intrinsic motivation in their teachers based on the knowledge of the factors that trigger it with strategies and techniques that influence the improvement of teachers' professional performance. Thus, the research provides a proposal for a human talent management model based on intrinsic motivation that influences the process of teachers' professional performance.
From the methodological point of view, the proposal includes the determination of the factors that awaken motivation, the creation of a culture of motivation and the establishment of strategies to remain intrinsically motivated in front of the tasks or activities that lead to be an important factor in the professional performance of teachers in service of the educational institutions and in particular in the educational institution Pedro Ruiz Gallo.
The model is organized holistically and systemically under a strategic human talent management approach in whose processes are linked the dimensional elements of human talent management by intrinsic motivation that are interrelated and integrated, giving rise to new dimensions, from which are born strategies that are drivers of awakening intrinsic motivation in people. All this is linked to the influence on professional teaching performance, motivational competence and organizational competitiveness.
Materials and methods
For the present research the descriptive design was used, the study population is made up of 19 collaborators among teaching staff and directors of the Primary and Secondary Educational Institution "Pedro Ruiz Gallo" - Mochumí, the sample is equal to the population. The technique used was the survey, the instrument used was the questionnaire on the variables under study, which allowed gathering information on the proposed model, applied directly to the study sample.
The procedures for data collection were developed in two stages. In the planning stage, the objective of the survey was defined according to the study problem, determination of the items, formulation of the questionnaire, validation of the expert judgment. In the field stage: coordination with the director of the educational institution for the respective authorization, application of the survey to teachers and collection of the surveys for subsequent tabulation and analysis, descriptive statistics or exploratory analysis of data according to the objectives and the hypothesis formulated, which allow us to detect the outstanding and unexpected characteristics of the research problem.
For the construction of the problem, the historical framework was used to describe, analyze and explain how the evolution of the facts of the study population is presented in time and space, and the Hypothetical Deductive method, logically concatenating with the entire research process from the stage of: diagnosis, planning, execution and presentation of results.
For the construction of the theoretical framework, the analytical method was used, which made it possible to know, through analysis and critical examination at an in-depth level, the theoretical and practical foundations of the study variables in order to: explain, make analogies, better understand their behavior and establish new theories; the inductive-deductive method, which made it possible to organize and accumulate knowledge and information in relation to the study variables. Deduction entailed establishing the relationship between theory and observation of the reality under study in order to establish the phenomena under investigation on the basis of the theory.
In this research, the minimum ethical criteria were considered, such as objectivity, honesty and respect for the rights of third parties, respecting the authorship of the authors, citing each of the sources consulted. There is coherence in the development of the phases of the research process, strengthening the objectivity in the quality of the research. Likewise, respect for the people involved in the collection of data within the educational institution. The results are handled in a prudent manner with the safety and well-being of the people involved in the research.
Results
A job performance questionnaire was applied and the results are presented below item by item, as well as by dimensions and by the general variable Performance.
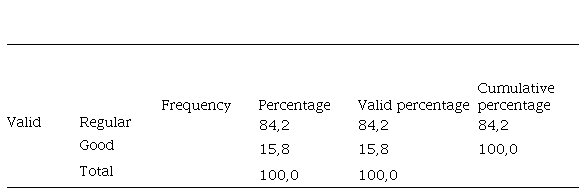
Professional development dimension (grouped)
We observe that the majority (84.21%) are located in the professional development dimension at the Regular level and (15.79%) are at the Good level.
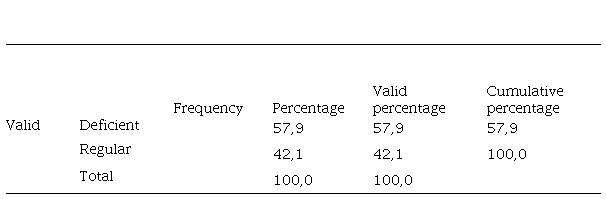
Dimension of teaching function and practice (grouped)
We observe that the majority (57.89%) are located in the teaching function and practice dimension at the Deficient level and 42.11% are at the Regular level.
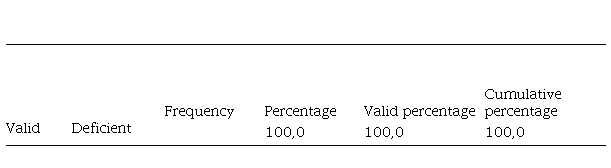
Performance Variable (grouped)
We observed that All (100%) have a deficient level of performance.
Therefore, in the diagnostic objective, both in the dimensions and in the general variable, teachers have difficulties in their performance, making it necessary to implement the model designed in this research, which is explained in the following section.
Discussion
According to the results of the Research, regarding the first objective it was determined that the decent performance in 100% came out deficient, which evidenced the situations observed at the beginning of the research, in deficiencies in the dimensions Function and teaching practice and development of professionalism, the same deficiencies can be observed in many organizations in which similar researches were also conducted such as Berrú, Campos, & Seminario (2013) who point out that job performance is also low, and at the same time point out in their study that one of the factors that is related to this is intrinsic, and that was one of the reasons to consider in the present work the design of a human talent management model by intrinsic motivation, precisely to develop teaching professional performance.
The model is based on the theories of strategic human talent management and competencies, and theories related to intrinsic motivation by Thomas Kenneth, Pink, Bandura's self-efficacy, Cskszentmihalyi's flow theory, and Deci Ryan's needs theory have also been considered; these theories supported the design of the phases that are given by a set of actions to comprehensively promote the development of the dimensions Internal, external, orientation towards the purpose and perseverance for mastery and autonomy of the Human Talent Management variable and the dimensions function and teaching practice and development of professionalism of the teaching performance variable that are incorporated in the designed model. The model was validated by experts who agreed on its construct and applicability.
References
Alvarez, L., Gudiño, L., Macías, M. e Izquierdo, H. (2020). Coaching educativo: desarrollo de competencias en el educando de nivel Superior. Formación docente - revista iberoamericana de educación. 3(2). http://www.revista-iberoamericana.org/index.php/es/article/view/36/101
Bedor, L. (2018). La formación continua de los docentes para la inclusión de los estudiantes con necesidades educativas especiales. Espirales revista multidisciplinaria de investigación. 2(20). https://www.revistaespirales.com/index.php/es/article/view/338/251
Berrú, N., Campos, J., y Seminario, E. (2013). Relación entre motivación intrínseca y satisfacción laboral de los docentes de la IE Albert Einstein College, 2013. (Tesis de maestría), Universidad Cesar Vallejo, Chiclayo.
Deci, L., y Ryan, R. (2002). Handbook of self-determination research. Rochester, NY: University of Rochester Press.
Dimaté, C., Tapiero, O., González, C., Rodriguez, R. y Arcila, M. (2017). La evaluación del desempeño docente. Revista Folios, (46), 83-95. https://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=3459/345951474007
Gamboa Romero, M. A., Barros Morales, R. L., & Barros Bastidas, C. (2016). La agresividad infantil, aprendizaje y autorregulación en escolares primarios. LUZ, 15(1), 105-114. Recuperado a partir de https://luz.uho.edu.cu/index.php/luz/article/view/743
Gomez, L. (2008). El Profesorado ante la conflictividad del ámbito Docente. Valencia, España: Universidad de Valencia.
Herzberg (1959) Las Competencias clave para una gestión integrada de recursos humanos (2 ed.). España: Deusto S.A.
Herrera, S. (2011). Motivación, satisfacción y clima laboral de los docentes de la IE Karl Weiss, Chiclayo, 2011. (Tesis de maestria), Universidad Cesar Vallejo, Chiclayo.
Lewis, R., y Heckman, R (2006). Talent management: A critical review. Human Resource Management Review, 16(2), p. 139
López, F. (2018). Gestión del talento humano basado en competencia en áreas de sociales. Centro Sur, 2(1). http://www.centrosureditorial.com/index.php /revista/article/view/8/7
López, F. y Narváez, J. (2019). Calidad en la educación superior basado en competencias en la universidad de Guayaquil hacia la formación del talento humano. Journal of business and entrepreneurial studies, 3(2), http://journalbusinesses.com/index.php/revista/article/view/21/43
Marcelo, C., y Vaillant, D. (2009). Desarrollo Profesional Docente. Madrid: Narcea, S.A. de Ediciones.
Marroquin, M. (2019) Análisis de las relaciones conceptuales de la identidad y la práctica profesional docente. Sinergias educativas, 4(2). http://sinergiaseducativas.mx/index.php/revista/article/view/42/53
Martínez, G. y Guevara, A. (2015). La evaluación del desempeño docente. Ra ximhai, 11(4), https://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=461/46142596007
Maslow, A. (1943). Eupsychian Management: A Journal. Richard D Irwin, Homewood, III.
McClelland, D. (1961). The Achieving Society. Princeton, NJ. D. Van Nostrand. Place of publication.
Molina, K. y García, C. (2018). Relación entre el estrés laboral y el área afectiva en los docentes de la Universidad Técnica de Manabí. Espirales revista multidisciplinaria de investigación. 2(16). https://www.revistaespirales.com/index.php/es/article /view/233/182
Moreno, C y Sánchez, L. (2019) Nuevo modelo para la gestión del talento humano.
Robbins, S. y (2005). Administración (8 ed.). (J. F. Davila Martinez, & M. A. Sánchez Carrión, Trads.) México: Pearson Educación de México, S.A. de C.V.
Rojas, E y Hernández, M (2020) Bachilleres, factores y políticas públicas hacia la educación superior. Caso Cachipay - Cundinamarca. Sinergias educativas, 5(1). http://sinergiaseducativas.mx/index.php/revista/article/view/65/148
Solís, P. (2019). Calidad en la educación superior basado en competencias en universidades públicas. Formación docente - revista iberoamericana de educación. 2(3). http://www.revista-iberoamericana.org/index.php/es/article/view/26/68

